- Перевеод на Дзен
-
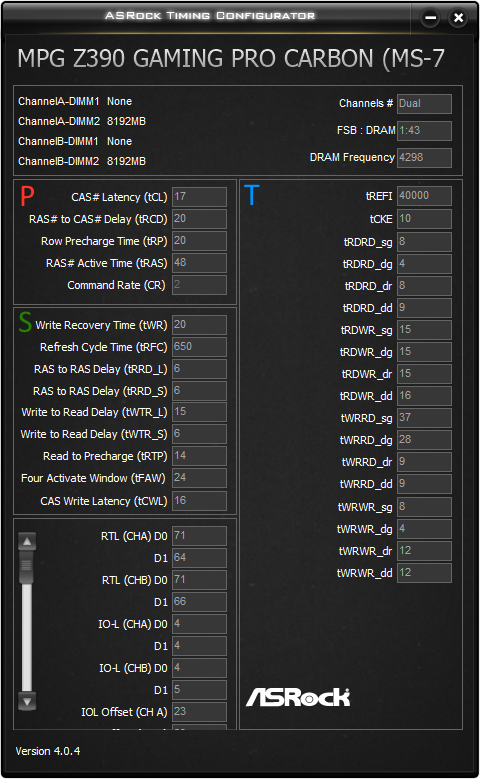
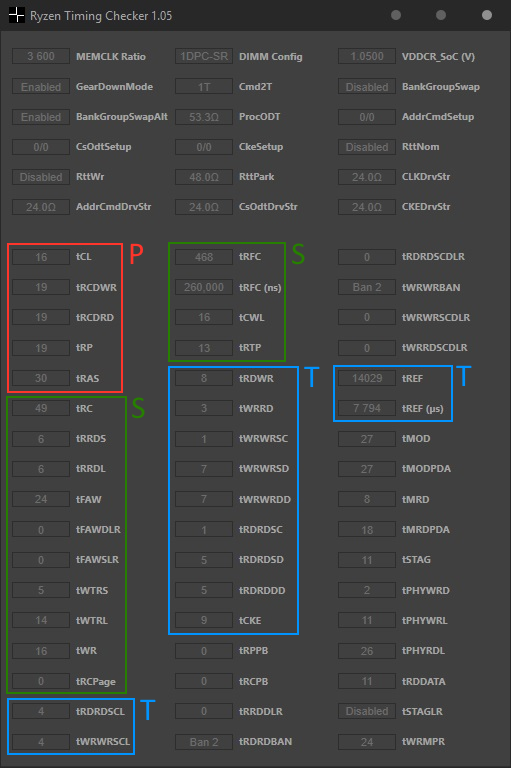
RAM timings are split into 3 categories: primary, secondary, and tertiary. These are indicated by ‘P’, ‘S’, and ‘T’, respectively.
- Primary and secondary timings affect latency and bandwidth.
- Tertiary timings affect bandwidth.
- The exception is tREFI/tREF, which affects latency and bandwidth, though it isn’t modifiable on AMD.
Motherboard
Motherboards with 2 DIMM slots will be able to achieve the highest frequencies.
For motherboards with 4 DIMM slots, the number of sticks installed will affect your maximum memory frequency.
On motherboards that use a daisy chain memory trace layout, 2 sticks are preferred. Using 4 sticks may significantly impact your maximum memory frequency.
On the other hand, motherboards that use T-topology will overclock the best with 4 sticks. Using 2 sticks won’t impact your maximum memory frequency as much as using 4 sticks on a daisy chain motherboard (?).
There are some T-topology motherboards that overclock as well or better with just one DIMM per channel.
Most vendors don’t advertise their memory trace layout, but you can make an educated guess based on the QVL. For example, the Z390 Aorus Master uses a T-Topology layout as its highest validated frequency is with 4 DIMMs. However, if the highest validated frequency were done with 2 DIMMs, it probably uses a daisy chain layout.
According to Buildzoid, Daisy Chain vs. T-Topology only matters above DDR4-4000. Following Buildzoid’s logic, if you’re on Ryzen 3000 or 5000, this doesn’t matter as DDR4-3800 is the typical max memory frequency when running MCLK:FCLK 1:1.
Lower end motherboards may not overclock as well, possibly due to the lower PCB quality and the number of layers (?).
- Single rank sticks usually clock higher than dual-rank sticks, but depending on the benchmark, the performance gain from rank interleaving1 can be significant enough to outperform faster single-rank sticks. This can be observed in synthetics and games.
- On recent platforms (Comet Lake and Zen3), BIOS and memory controller support for dual-rank has significantly improved. On many Z490 boards, dual rank Samsung 8 Gb B-die (2×16 GB) will clock just as high as single-rank B-die, meaning you have all the performance gains of rank interleaving with little to no downsides.
- 1Rank interleaving allows the memory controller to parallelize memory requests, for example writing on one rank while the other is refreshing. The impact of this is easily observed in AIDA64 copy bandwidth. From the eyes of the memory controller, it doesn’t matter whether the second rank is on the same DIMM (two ranks on one DIMM) or a different DIMM (two DIMM in one channel). It does, however, matter from an overclocking perspective when you consider memory trace layouts and BIOS support.
- Having a second rank of the same IC also means twice as many bank groups are available. That means that short timings – such as RRD_S rather than RRD_L – can be used more often, as it’s more likely for there to be a fresh bank group available. The long timing (L) is required when operating on the same bank group twice in a row, and when there are 7 other bank groups instead of 3 you have a lot more choices to avoid doing that.
- It also means that there are twice as many banks, and thus twice as many memory rows can be open at any given time. As a result, it’s more likely that the row you need will be open. You won’t have to close row A, open row B, and then close B to open A again as often. You’re held up by operations like RAS/RC/RCD (when waiting for a row to open because it was closed) and RP (when waiting for a row to close to open another one) less often.
- x16 configurations will have half as many banks and bank groups as the traditional x8 configurations, which means less performance. See buildzoid’s video for more information.
- Density matters when determining how far your ICs can go. For example, 4 Gb AFR and 8 Gb AFR will not overclock the same despite sharing the same name. The same can be said for Micron Rev. B, which exists as 8 Gb and 16 Gb. The 16 Gb ICs overclock better and are sold in 16 GB and 8 GB capacities despite the DIMMs using 8 chips. The 8 GB sticks have their SPD modified and can be found in higher-end Crucial kits (BLM2K8G51C19U4B).
- As the total count of ranks in a system increases, so does the load on the memory controller. This usually means that more memory ranks will require higher voltage, especially VCCSA on Intel and SOC voltage on AMD.
-
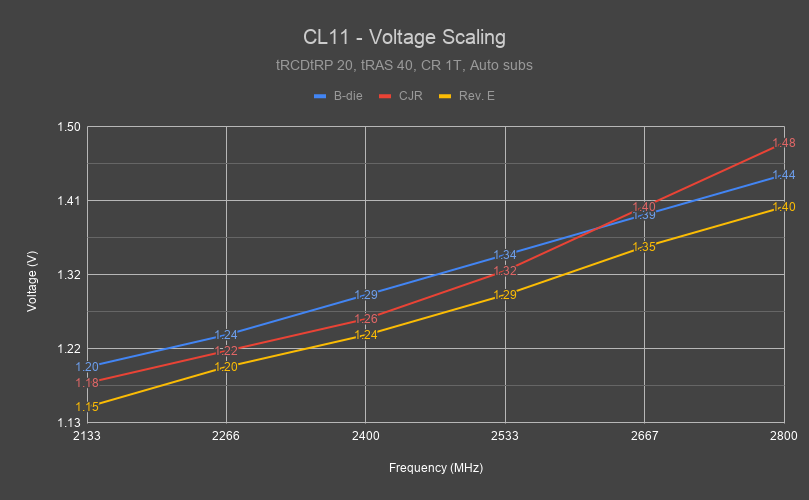
Voltage scaling simply means how the IC responds to voltage.
-
On many ICs, tCL scales with voltage, meaning giving it more voltage can allow you to drop tCL. Conversely, tRCD and/or tRP typically do not scale with voltage on many ICs, meaning no matter how much voltage you pump into it, it will not budge.
As far as I know, tCL, tRCD, tRP, and possibly tRFC can (or can not) see voltage scaling. -
Similarly, if a timing scales with voltage, you can increase the voltage to run the same timing at a higher frequency.

Максимальное рекомендуемое напряжение DDR4.
JEDEC JESD79-4B (стр. 174) указывает, что абсолютный максимум составляет 1,50 В. Такое высокое напряжение нельзя подавать на душманские плашки.